Breakouts in adults are extremely common, even if your skin was perfectly clear while you were a teenager.
What causes these breakouts?
There are a few different factors that could lead to them, but one in particular has been identified as quite the trigger…
What is Gluten?
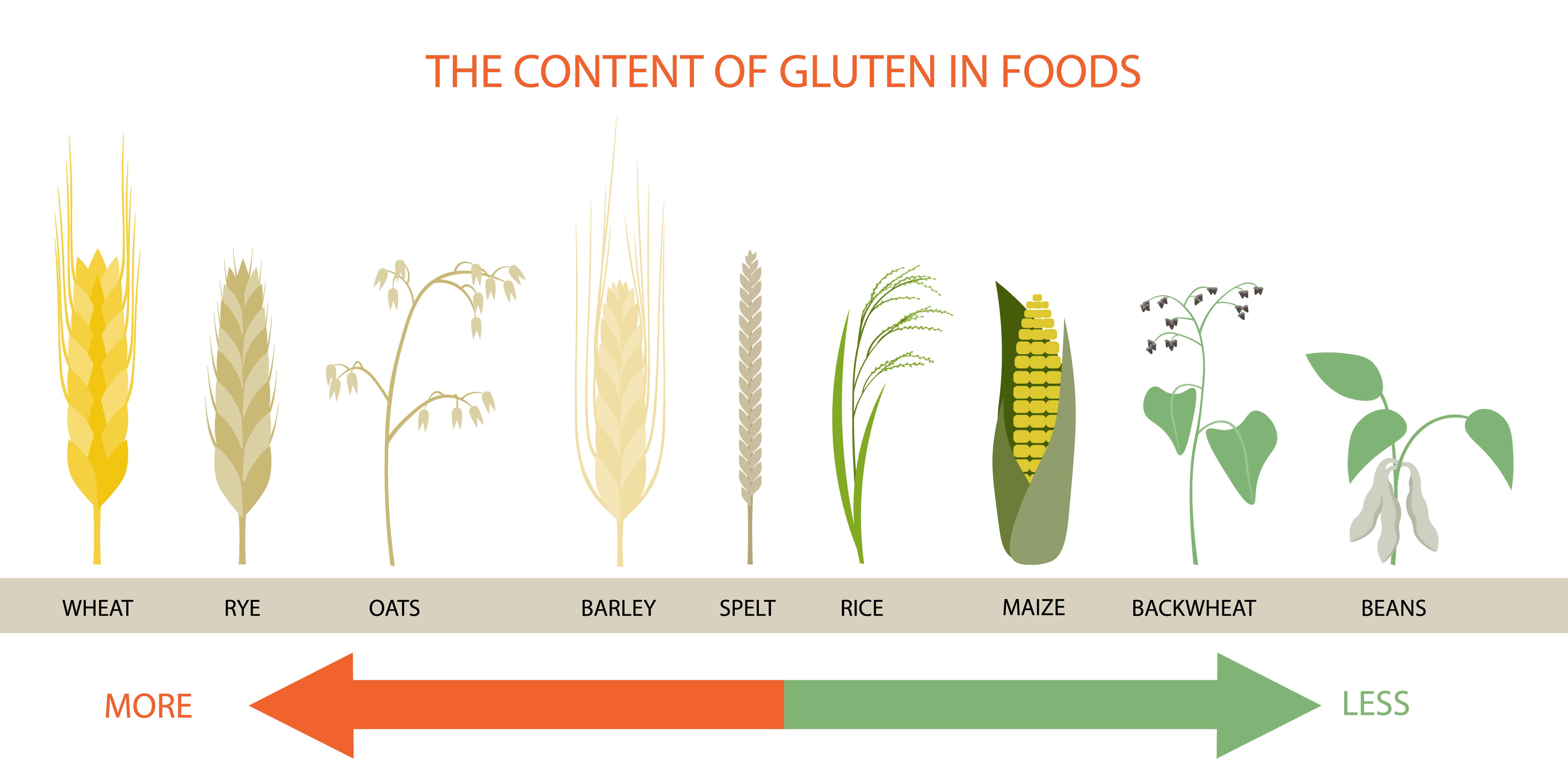
Gluten refers to the proteins found in wheat, as well as other cereal grains, such as rye and barley. It can also be found in the majority of other foods out there, including fruits and vegetables, but the amount of gluten in those is tiny compared to what can be found in grains.
Gluten is what gives bread dough its sticky consistency, and, because of this unique quality, gluten is now also used in a number of other products, from shampoo to toothpaste.
While this may be the case, the majority of your exposure to gluten will come from the foods that you eat.
Gluten Sensitivity and Celiac Disease
Around 1% of the population is severely intolerant to gluten. This means that when gluten is consumed, an immediate, and often painful, reaction is experienced.
This is referred to as celiac disease, and symptoms include:
- Bloating
- Gas
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Fatigue
- Weight loss
- Depression
Since the symptoms of celiac disease are quite severe, it is usually quite easy to determine whether or not this is a condition that someone is suffering for.
However, when it comes to a milder gluten sensitivity, this can be slightly trickier…
For those who are gluten sensitive, symptoms don’t usually appear straight away, and can instead build up over time.
This then leads to:
- Skin problems
- Digestive problems
- Weakness
- Pain in the muscles and joints
- Neurological problems
There are over 300 minor symptoms that are a sign of a mild gluten sensitivity, and it is believed that around 18 million Americans are suffering from this, leading to a rapid growth in the gluten-free food industry.
The Connection Between Gluten and Acne
In order to understand the connection between gluten and acne, it is important to know more about how your body reacts when gluten is consumed.
When gluten enters into your body, your intestines react by producing a substance known as zonulin, which creates small gaps in the lining of your gut. This means that when toxins, as well as larger gluten molecules, travel through your intestines, they end up escaping through these cracks and entering back into your bloodstream.
What happens then?
Your immune system responds by creating inflammation in your body, since it believes that the gluten is an invader that needs to be destroyed.
That isn’t the end of the story…
As time goes on and this happens more and more, your gut ends up becoming quite permeable. This means that everything from bacteria to other dietary proteins escape through the gut lining rather than passing straight through, and all of this then ends up in your bloodstream. This triggers even more of a reaction from your immune system, resulting in severe inflammation.
What does this have to do with acne?
Well, while there is a lack of research on the direct link between gluten and acne, it goes without saying that this chronic inflammation in itself can have quite an effect on your skin.
How?
One of the main ways is the increased skin pH level that inflammation causes. This then makes your skin an ideal breeding ground for bacteria and other unwanted substances, resulting in clogged pores and breakouts.
Want to lower your pH level back down?
The foods that you eat play a significant role in this, but you can also try to find a pH balancing skin cleanser. These will feature either a neutral or a slightly acidic pH level, in order to balance out the pH level on the surface of your skin.
The inflammation caused by gluten also damages your skin’s outer protective layer, meaning that even more bacteria is able to directly enter the skin and trigger a breakout.
But wait, there’s more…
Cereal grains are carbohydrates, and when you consume them, they cause your blood sugar levels, as well as your insulin, to rise. This then stimulates the body into releasing IGF-1, which is a growth factor that then causes your body to release certain hormones, such as testosterone.
Don’t worry, this isn’t going to cause you to suddenly grow facial hair, as you would need a lot more testosterone for that. However, the small amount that is released does have an impact, usually when it comes to your skin’s sebaceous glands. It triggers your oil glands to produce more sebum, resulting in oilier skin, clogged pores and more acne.
Not All Acne is Caused By Gluten
While there does seem to be quite a solid link between gluten and acne, keep in mind that this won’t be applicable for everyone.
Some people are able to tolerate gluten just fine, meaning that their immune system doesn’t react to it and the above problems are not experienced.
However, those who suffer from a gluten sensitivity are more likely to experience breakouts caused by gluten, due to the way in which the gluten affects their immune system.
Other Skin Issues Caused by Gluten
As you have learned, gluten leads to a number of internal changes in your body, and acne is just one of the side effects that come from this.
Wondering how else gluten affects your skin?
Here are a few common skin conditions that can either be caused or exacerbated by gluten:
- Atopic Dermatitis – also known as eczema, there is a strong link between this condition and gluten sensitivities
- Psoriasis – this condition is caused by reactions in the immune system, and the National Psoriasis Foundation recommends that those suffering from the condition reduce their gluten consumption in order to clear their symptoms
- Vitiligo – refers to lost pigment in the skin, resulting in light or white patches appearing. Studies show that going gluten-free can help to bring the natural pigmentation back to the skin
Going Gluten-Free
Do you suspect that gluten may be causing your acne?
If so, it may be worth trying to reduce the amount of gluten you eat.
Worried that this will leave you lacking in nutrients?
Not at all. Humans don’t need to eat grains, and can enjoy a fully balanced and healthy diet even by completely cutting grains out of their life.
Wondering how to get started with going gluten-free?
Let’s begin by talking about the many packaged gluten-free foods that are now available…
These may seem like an easy option, especially if you are confused about what a gluten-free diet actually consists of. However, all of those gluten-free pizzas, brownies, biscuits and everything else are packed with sugars and refined grains, and actually feature even more calories than their gluten-containing alternatives.
So, what should you eat instead?
Well, it’s probably easier to first look at the foods that you shouldn’t eat, which include:
- Wheat
- Barley
- Rye
- Oats
- Corn
- Energy bars that contain the above
- Soups that contain flour
- Salad dressings and marinades
- Soy sauce
- Vegan meat alternatives
- Flavored nuts and chips
- Some medications
Remember that gluten is often used as a thickener for different foods, so even if you wouldn’t expect something to contain gluten, it is always worth checking the ingredients list. While companies are required to state whether their products contain dairy or nuts, there are no regulations at the moment for gluten, so you will need to exert some vigilance yourself.
Worried that there’s nothing left for you to eat?
The list above may seem long, but a gluten-free diet is actually pretty easy to put together.
Some ideas include:
- Fresh fruits and vegetables
- Beans, nuts and seeds
- Fish
- Lean meat
- Gluten-free grains, such as rice, millet, buckwheat and quinoa
There is no denying that going gluten-free can sometimes be challenging at first, and does require a bit of extra planning when it comes to your meals. If you are worried about nutritional deficiencies, it may be worth visiting a dietician to put together a healthy gluten-free diet plan.
Should you be giving up gluten if you don’t have a gluten sensitivity?
With the effects of gluten becoming more widely understood, many believe that gluten is something that nobody should be eating, whether they suffer from a gluten sensitivity or not.
Not only that, but the rise in the gluten-free market has led these foods to be perceived as quite trendy, meaning that more and more people are jumping on the gluten-free bandwagon, even if they don’t need to.
Should you be doing this too?
No, if you don’t suffer from a gluten sensitivity then there is no need to give up gluten. While cutting back on gluten won’t hurt, you need to make sure that your body is still receiving all of the nutrients that it needs. Many common gluten foods, such as fortified bread and cereal, contain vital vitamins, such as the B vitamin complex, which many are actually deficient in.
Unless you are prepared to take the time to ensure that your diet is well-rounded, giving up gluten is not something that you need to do.
Improving Gut Health
As mentioned above, gluten can negatively impact the health of your gut and immune system, especially since 80% of your immune system is located in your GI tract.
If you have a gluten sensitivity but don’t want to completely give up gluten, working on improving the overall health of your gut can reduce some of the symptoms that gluten causes. Even if you don’t have a gluten sensitivity, boosting your gut health will improve your overall health, as well as the appearance of your skin.
How can you strengthen your gut?
Here are a few tips:
- Eat plenty of fruits, vegetables, beans and legumes – these foods contain high amounts of fiber, which specific types of beneficial bacteria in your gut feed on in order to grow
- Fermented foods – from kimchi and sauerkraut to kefir and kombucha, fermented foods contain a variety of good bacteria strains, all of which will help to balance out any bad bacteria in your gut. Yogurt is another fermented food, but make sure you opt for one as least processed as possible, in order to preserve its beneficial bacteria. Flavored yogurts that are packed with sugar should be avoided
- Prebiotics – these basically feed the probiotics in your body, which then feed the beneficial bacteria. Prebiotics can be found in several different foods, including garlic, onions, asparagus, dandelion greens and chicory root. Prebiotic supplements can also be beneficial
- Polyphenols – these are compounds found in plants that are fantastic for reducing inflammation and oxidative stress. They are also digested by the gut bacteria, enabling the good bacteria strains to thrive. Polyphenols can be found in high concentrations in dark chocolate, red grapes, green tea, almonds, blueberries and broccoli
- Cut back on junk food and alcohol – both of these will negatively impact the health of your gut
Good bacteria in your gut will strengthen your gut’s lining, which is something that gluten damages. Research has shown that improving gut health has a significant impact on the skin, clearing it up and giving it a healthy glow.
Gluten has been in the headlines so much lately, and this has led to an increasing number of people going gluten-free. For those of you who suffer from a gluten sensitivity, giving up gluten will likely lead to an improvement in your acne. However, for everyone else, it is probable that your acne is caused by another factor, and while giving up gluten won’t hurt, it would be more beneficial if you were able to identify the exact cause of your acne, so that you can then work on tackling that.








Leave A Comment